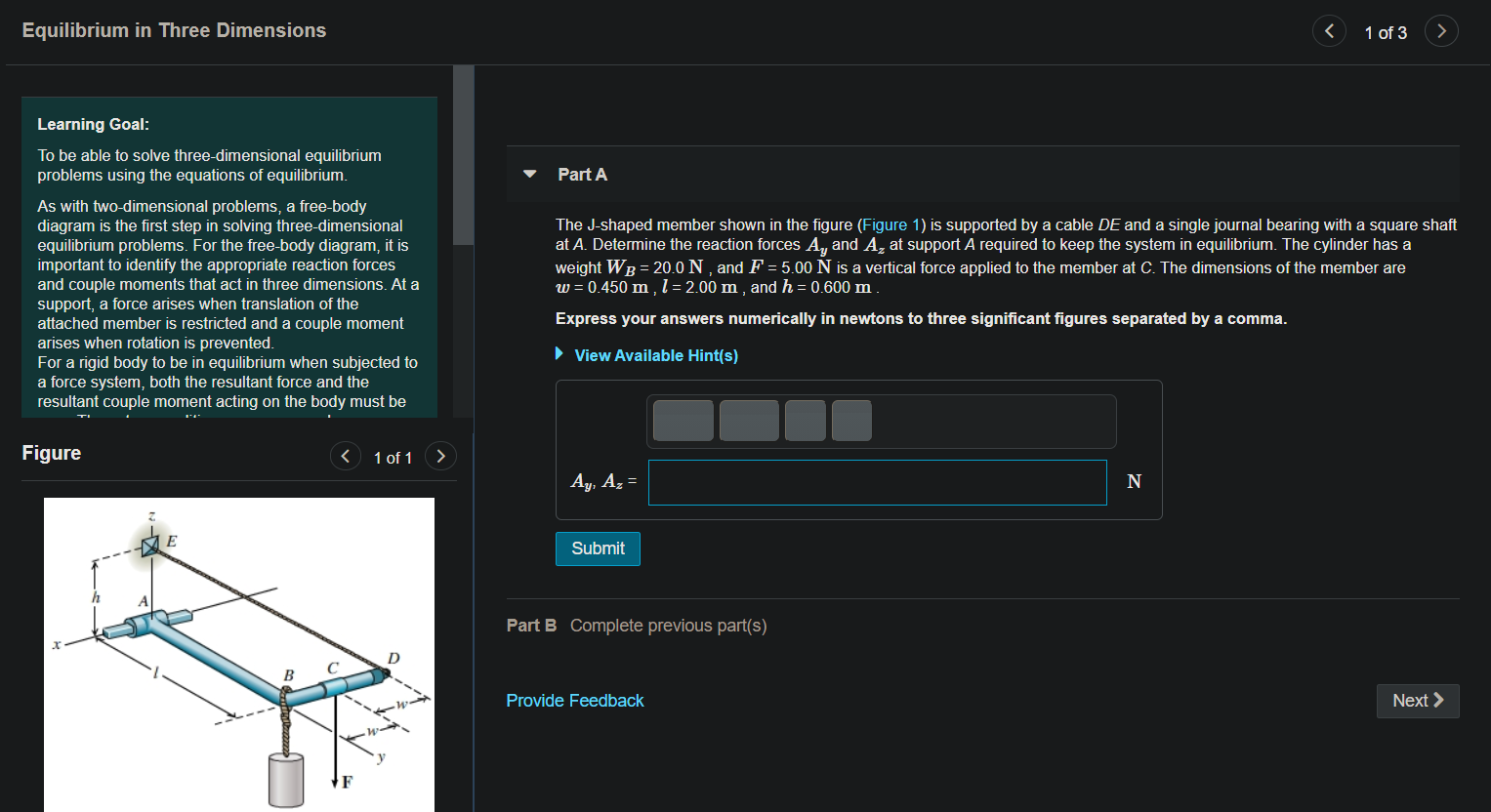
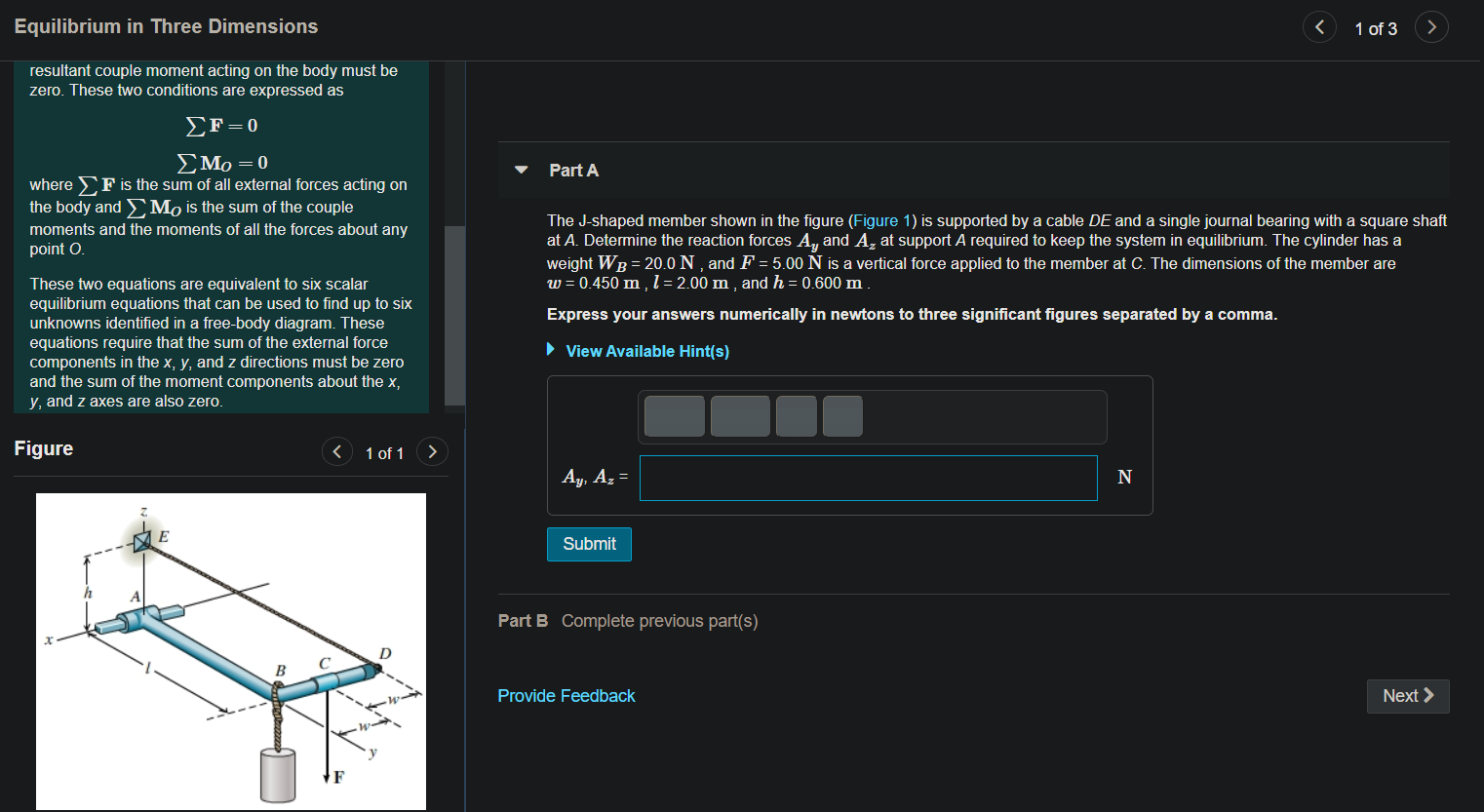
Equilibrium in Three Dimensions < 1 of 3 Part A Learning Goal: To be able to solve three-dimensional equilibrium problems using the equations of equilibrium. As with two-dimensional problems, a free-body diagram is the first step in solving three-dimensional equilibrium problems. For the free-body diagram, it is important to identify the appropriate reaction forces and couple moments that act in three dimensions. At a support, a force arises when translation of the attached member is restricted and a couple moment arises when rotation is prevented. For a rigid body to be in equilibrium when subjected to a force system, both the resultant force and the resultant couple moment acting on the body must be The J-shaped member shown in the figure (Figure 1) is supported by a cable DE and a single journal bearing with a square shaft at A. Determine the reaction forces A, and A, at support A required to keep the system in equilibrium. The cylinder has a weight WB = 20.0 N, and F =5.00 N is a vertical force applied to the member at C. The dimensions of the member are w = 0.450 m , l = 2.00 m , and h = 0.600 m Express your answers numerically in newtons to three significant figures separated by a comma. View Available Hint(s) Figure < 1 of 1 > Ay, Az = N Submit Part B Complete previous part(s) D Provide Feedback Next > F
Equilibrium in Three Dimensions 1 of 3 resultant couple moment acting on the body must be zero. These two conditions are expressed as ΣF = 0 Mo=0 where F is the sum of all external forces acting on the body and Mo is the sum of the couple moments and the moments of all the forces about any point o. Part A The J-shaped member shown in the figure (Figure 1) is supported by a cable DE and a single journal bearing with a square shaft at A. Determine the reaction forces Ay and A, at support A required to keep the system in equilibrium. The cylinder has a weight WB = 20.0 N, and F =5.00 N is a vertical force applied to the member at C. The dimensions of the member are w=0.450 m , 1 = 2.00 m, and h = 0.600 m. Express your answers numerically in newtons to three significant figures separated by a comma. These two equations are equivalent to six scalar equilibrium equations that can be used to find up to six unknowns identified in a free-body diagram. These equations require that the sum of the external force components in the x, y, and z directions must be zero and the sum of the moment components about the x, y, and z axes are also zero. View Available Hint(s) Figure 1 of 1 > Ay, Az = N Submit Part B Complete previous part(s) D Provide Feedback Next >
没有找到相关结果