
Consider a population of N diploid individuals (with two copies of their genetic materialin each cell).We study two linked loci,where the first locus can be occupied by either oneof two alleles A and a that have the same fitness,and the second locus can be occupied byeither one of two alleles B and b of the same fitness.Thus,we have ten different genotypes:AAAAAAAaAaAaAa22aaBBBbbbBBBbbBbbBBBbbbHere the first row is the first locus and the second row is the second locus,while the columnsrepresent the two homologous chromosomes in the diploid population.Also,the chromosomeAaaAordering is irrelevant:e.g.andare indistinguishable.bBBbWe enumerate these genotypes by the integers from 0 to 9.The population in generation tcan be thought as a ten-dimensional vectorX(t)=(Xo(t),x1(t),x2(t),x3(t),X4(t),X(t),x(t),x7(t),Xg(t),xg(t),where X(t)is the respective population of genotype k.We assume the population is of fixedsize:Xo(t)+X1(t)+X2(t)+X3(t)+X4(t)+X5(t)+X6(t)+X7(t)+X8(t)+X9(t)=N.In the process of formation of the next generation t+1,the individuals in generation tproduce (segregate)gametes.Two gametes will then join to form an individual of the nextaAageneration.For example,BorBwill merge intoBB
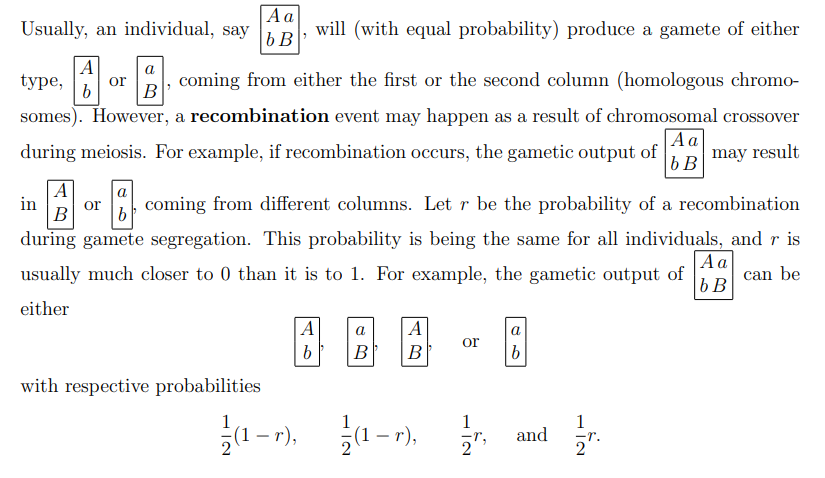
AaUsually,an individual,saybBwill (with equal probability)produce a gamete of eitherAatype,borBcoming from either the first or the second column (homologous chromo-somes).However,a recombination event may happen as a result of chromosomal crossoverAaduring meiosis.For example,if recombination occurs,the gametic output ofbBmay resultinBorbcoming from different columns.Let r be the probability of a recombinationduring gamete segregation.This probability is being the same for all individuals,and r isAausually much closer to 0 than it is to 1.For example,the gametic output ofcan bebBeitherAaAabBBorbwith respective probabilities11112(1-r)-2T),2and2T.

We extend the Wright-Fisher model to the case of two loci.Here,each individual in gener-ation t+1 is produced by randomly selecting two individuals in generation t.Each of themsegregates a gamete,and the gametes are joined to form a new individual.This is doneuntil we have N individuals in generation t+1.And so on,from one generation to the nextgeneration.Problem 1.Suppose X(t)=i,wherei=(io,i1,i2,i3,i4,is,i6,i7,ig,ig),where io+i+i2+i3+i4+is+i6+i7+i8+ig=N.Find the (conditional)probabilities pk(i)(k 0,...,9)for the new individual in populationt +1 to be of genetic type k.Problem 2.Find the general form for the transition probabilities in this modified Wright-Fisher modelp(i,j)=P(X(t+1)=j|X(t)=i)fori=(io,i1,i2,i3,i4,is,i6,i7,ig,ig),where io+i1+i2+i3+i4+is+i6+i7+ig+ig=N,andj=(j0,j1,j2,j3,j4,j5,36,j7,j8,j9),where jo+j1+j2+3+j4+j5+j6+j7+j8+j9=N.Hint:use pk(i)in Problem 1 and multinomial coefficients (and multinomial distribution).This should be similar to the single locus Wright-Fisher model,where binomial coefficientsand binomial distribution were used.
没有找到相关结果